The rhythmic crash of waves, a comforting sound for many, holds a more ominous tone as climate change affects sea levels . It's not just about losing beaches; it's about homes, economies, and entire ecosystems. This rising threat is fueled by melting glaciers and thermal expansion, demanding our immediate attention. This article explores the key mechanisms behind sea level rise , its far-reaching consequences, and what we can do to mitigate its impact. Discover how climate change affects sea levels and what it means for our future. (Understand how climate change affects sea levels. Explore the causes, impacts on coastal communities, and what we can do to mitigate this rising threat. Learn more today!)
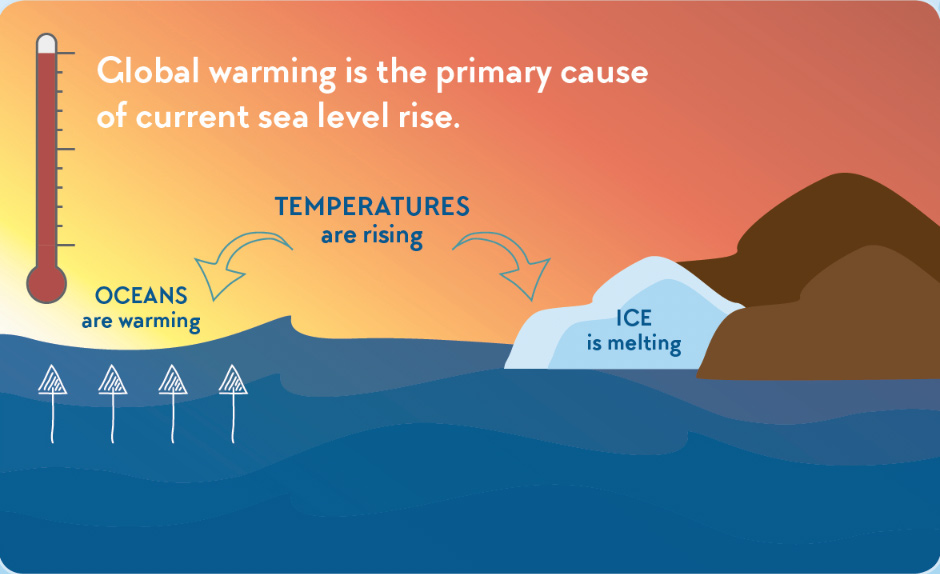
Let's break down how climate change is directly linked to rising sea levels. The two main culprits are thermal expansion and melting ice. Thermal expansion happens because water expands when it gets warmer. As our oceans absorb over 90% of the excess heat from greenhouse gas emissions, the water's volume increases. Simultaneously, glaciers and ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica are melting at an alarming rate, adding even more water to the oceans. The combination of these factors is creating a serious problem for coastal communities worldwide.
Now, how climate change affects sea levels comes down to a fundamental understanding of the greenhouse effect. As we burn fossil fuels, we release greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, warming the planet, which in turn leads to both thermal expansion and ice melt. Scientists use climate models to predict future sea level rise, but the exact amount is uncertain due to factors like the rate of ice sheet melt. However, the consensus is clear: sea levels will continue to rise unless we drastically reduce our greenhouse gas emissions.
In essence, the story of how climate change affects sea levels is a complex one with profound implications. From thermal expansion to melting glaciers, the mechanisms are clear. The question now is what we will do with this information. It's not a matter of if sea levels will rise, but how much and how quickly. We need to reduce emissions, adapt to the changes already underway, and protect vulnerable communities. Our response to this challenge will determine the future of our coastlines and the people who call them home.
Understanding the Science
The Major Contributors to Sea Level Rise
Thermal Expansion: A Gradual Swelling
The ocean's ability to absorb heat is a double-edged sword. While it helps to moderate global warming, it also leads to thermal expansion. As the ocean warms, the water molecules move faster and take up more space. It might seem like a small effect, but when you consider the vastness of the ocean, even a slight increase in volume can translate to significant sea level rise. Think of it like heating up a pot of water; it overflows, but on a much larger scale.
Melting Glaciers and Ice Sheets: Adding Water to the Mix
The dramatic images of glaciers calving into the ocean are a stark reminder of the impact of climate change. Glaciers and ice sheets, which hold vast amounts of frozen water, are melting at an accelerating rate due to rising temperatures. This meltwater flows into the ocean, directly contributing to sea level rise. Greenland and Antarctica, in particular, hold enough ice to raise global sea levels by tens of meters if they were to melt completely.
Measuring Sea Level Rise: How Do We Know?
Scientists use a variety of methods to track sea level rise, including:
Tide Gauges: These traditional instruments measure the height of the water relative to a fixed point on land. While tide gauges provide long-term data, they only offer local measurements. Satellite Altimetry: Satellites equipped with radar altimeters measure the distance between the satellite and the sea surface. This provides a global view of sea level changes with high accuracy. GPS (Global Positioning System): GPS is used to track the vertical movement of land, which is important for correcting tide gauge measurements and understanding local sea level changes.
Climate Models: Predicting the Future
Climate models are complex computer simulations that use mathematical equations to represent the Earth's climate system. These models incorporate data on temperature, precipitation, sea level, and other factors to project future climate scenarios. While climate models have limitations, they are the best tools we have for understanding and predicting the impacts of climate change, including sea level rise.
The Impacts of Rising Sea Levels
Coastal Erosion and Inundation: Losing Ground
One of the most visible impacts of rising sea levels is coastal erosion. As sea levels rise, waves can reach further inland, eroding beaches, dunes, and other coastal landforms. This erosion can threaten homes, infrastructure, and ecosystems. Inundation, or permanent flooding, is another major concern, particularly for low-lying coastal areas.
Saltwater Intrusion: Contaminating Fresh Water
As sea levels rise, saltwater can infiltrate freshwater aquifers and rivers, contaminating drinking water supplies and damaging agricultural lands. Saltwater intrusion can have devastating consequences for coastal communities that rely on freshwater resources. This is a huge issue, especially in areas where freshwater is already scarce.
Impacts on Coastal Ecosystems: A Delicate Balance Disrupted
Coastal ecosystems, such as salt marshes, mangroves, and coral reefs, are highly sensitive to changes in sea level. Rising sea levels can inundate these habitats, leading to loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services. For example, salt marshes provide important habitat for many species of birds and fish, while mangroves protect coastlines from erosion. The loss of these ecosystems can have cascading effects throughout the food web.
Economic Consequences: The Price of Inaction
The economic consequences of rising sea levels are far-reaching. Coastal flooding and erosion can damage infrastructure, disrupt tourism, and displace communities. The costs of adapting to rising sea levels, such as building seawalls and relocating infrastructure, can be substantial. The longer we delay action on climate change, the higher these costs will become.
What Can We Do?
Mitigation: Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The most important thing we can do to address rising sea levels is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This requires a global effort to transition to clean energy sources, improve energy efficiency, and reduce deforestation. We need to hold governments and corporations accountable for their actions and advocate for policies that promote sustainability.
Adaptation: Preparing for the Inevitable
Even if we drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions today, sea levels will continue to rise for decades due to the inertia of the climate system. Therefore, we also need to adapt to the changes that are already underway. This includes building seawalls, restoring coastal habitats, and developing early warning systems for coastal flooding.
Community Action: Working Together
Addressing rising sea levels requires a collective effort. Communities need to come together to develop adaptation plans, advocate for policies that protect coastal resources, and educate their residents about the risks of climate change. Individual actions, such as reducing energy consumption and supporting sustainable businesses, can also make a difference.
FAQ: Your Questions Answered
Basic Understanding of How Climate Change Affects Sea Levels
What exactly causes sea levels to rise? Sea levels are rising due to two main factors: thermal expansion of water as it warms and the addition of water from melting glaciers and ice sheets. Climate change accelerates both of these processes.
Is sea level rise happening everywhere at the same rate? No, sea level rise varies regionally due to factors such as land subsidence, ocean currents, and gravitational effects. Some areas are experiencing more rapid sea level rise than others.
How much are sea levels expected to rise in the future? The amount of future sea level rise depends on future greenhouse gas emissions. Under high-emission scenarios, sea levels could rise by several feet by the end of the century.
Impacts and Consequences
What are the main dangers of sea level rise for coastal communities? Coastal communities face increased risks of flooding, erosion, saltwater intrusion, and displacement due to rising sea levels. How climate change affects sea levels directly endangers their livelihoods.
How does saltwater intrusion affect agriculture? Saltwater intrusion can contaminate freshwater sources used for irrigation, making it difficult to grow crops. It can also damage soil structure and reduce crop yields.
Are there any ecosystems that are particularly vulnerable to sea level rise? Yes, coastal ecosystems such as salt marshes, mangroves, and coral reefs are highly vulnerable to sea level rise. These ecosystems provide important habitat for many species and protect coastlines from erosion.
Mitigation and Adaptation
What can individuals do to help mitigate sea level rise? Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint by conserving energy, using public transportation, eating less meat, and supporting sustainable businesses. Understanding how climate change affects sea levels is the first step toward action.
What are some examples of adaptation measures that coastal communities can take? Coastal communities can build seawalls, restore coastal habitats, elevate buildings, and relocate infrastructure to higher ground.
Is it too late to do anything about sea level rise? No, it's not too late. While some sea level rise is already inevitable, we can still limit the amount of future sea level rise by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Every action we take to reduce emissions makes a difference.
Scientific Details
What is the role of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in understanding sea level rise? The IPCC is the leading international body for assessing climate change. It synthesizes the latest scientific research on sea level rise and provides policymakers with information to make informed decisions.
How do scientists use climate models to predict sea level rise? Climate models use mathematical equations to simulate the Earth's climate system. These models incorporate data on temperature, precipitation, sea level, and other factors to project future climate scenarios, including sea level rise.
What is the difference between relative sea level rise and global sea level rise? Global sea level rise refers to the average increase in sea level around the world. Relative sea level rise refers to the change in sea level at a specific location, which can be affected by local factors such as land subsidence.
The Future of Our Coasts
How climate change affects sea levels is a stark reality that demands our attention and action. The rising tides pose a significant threat to coastal communities, ecosystems, and economies around the world. Understanding the science behind sea level rise and the impacts it will have is crucial for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
While the challenges are daunting, there is still hope. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, adapting to the changes already underway, and working together as a global community, we can protect our coasts and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come. The time to act is now.
.png)