Alright, buckle up, because we're diving deep into something that affects literally everyone : The Future Impacts of Climate Change: Projections . Ever wonder what the world will look like for your grandkids? Explore future climate change projections. Understand the impacts on our planet, from rising sea levels to extreme weather. Learn how we can prepare and mitigate these effects. It's not some far-off sci-fi movie; it's happening now, just gradually enough that sometimes it feels like we can ignore it. But ignoring it is definitely not an option. So, let’s take a look at what the experts are predicting, and what we can actually do about it.
We’re talking about shifts in weather patterns, more frequent and intense extreme weather events, rising sea levels threatening coastal communities, disruptions to agriculture and food security, and the potential displacement of millions of people. Thinking about The Future Impacts of Climate Change: Projections isn't just about understanding the science; it's about understanding the human cost, the economic consequences, and the potential for social and political instability. It’s about recognizing that climate change isn’t just an environmental issue; it’s a multifaceted crisis that touches every aspect of our lives.
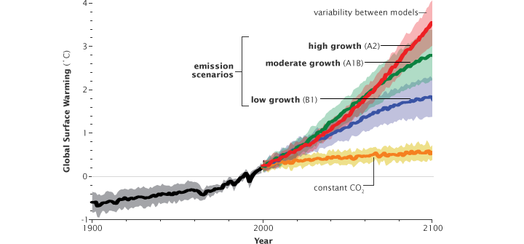
So, what exactly are The Future Impacts of Climate Change: Projections trying to tell us? Scientists use complex climate models to simulate how the Earth's climate system will respond to different levels of greenhouse gas emissions. These models take into account a vast array of factors, from atmospheric processes to ocean currents to land surface interactions. The goal is to provide policymakers and the public with the best possible information about the range of potential future climate outcomes, so we can make informed decisions about how to respond. It's about giving us a heads-up on what’s coming, so we can hopefully soften the blow.
The Future Impacts of Climate Change: Projections reveal a world facing significant challenges. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events like hurricanes and droughts are all but guaranteed. Coastal regions will face inundation from rising sea levels, threatening communities and infrastructure. Agriculture will struggle to adapt to changing conditions, leading to food shortages and price increases. These consequences necessitate urgent action. The scale of these impacts demands immediate and concerted efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the changes already underway.
Understanding Climate Projections
What Are Climate Models?
Climate models are sophisticated computer programs that simulate the Earth's climate system. They use mathematical equations to represent the physical, chemical, and biological processes that drive the climate. These models are based on fundamental scientific principles and are constantly being refined and improved as our understanding of the climate system grows. Think of it like a super-powered weather forecast, but for the long term.
How Do They Work?
Climate models divide the Earth into a grid and calculate the interactions between different components of the climate system, such as the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and ice. They take into account factors like greenhouse gas concentrations, solar radiation, and volcanic eruptions. By running these models under different scenarios of future emissions, scientists can project how the climate will change in the coming decades and centuries. They aren’t crystal balls, but they’re the best tool we have.
Limitations of Climate Models
It's crucial to recognize that climate models are not perfect. They are complex systems with inherent uncertainties. They can struggle to accurately represent certain processes, such as cloud formation and small-scale weather events. Furthermore, the future is inherently uncertain, and the projections depend on assumptions about future emissions, technological developments, and policy decisions. That’s why scientists present a range of possible outcomes, rather than a single definitive prediction.
Key Projections and Their Implications
Temperature Increases
One of the most consistent and well-established projections is that global temperatures will continue to rise. The amount of warming will depend on future greenhouse gas emissions. Even under optimistic scenarios, where emissions are significantly reduced, some further warming is unavoidable due to the inertia of the climate system. Under high-emission scenarios, the warming could be catastrophic, leading to widespread impacts on ecosystems, agriculture, and human health. We're talking heatwaves that are practically unsurvivable, especially for vulnerable populations.
Sea Level Rise
Sea level rise is another major concern. As the planet warms, glaciers and ice sheets melt, and the ocean expands due to thermal expansion. This leads to rising sea levels that threaten coastal communities and ecosystems. The rate of sea level rise is accelerating, and projections suggest that it could reach several feet by the end of the century, potentially displacing millions of people and inundating valuable infrastructure. Imagine entire cities being underwater – it’s that serious.
Extreme Weather Events
Climate change is projected to increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. This includes heatwaves, droughts, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires. These events can have devastating impacts on human lives, infrastructure, and the economy. They can also exacerbate existing social and economic inequalities, as vulnerable populations are often disproportionately affected. We're already seeing more extreme weather, and it's only going to get worse unless we take action.
Impacts on Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Climate change poses a significant threat to ecosystems and biodiversity. As temperatures rise and precipitation patterns change, many species will struggle to adapt. Some species may be able to migrate to more suitable habitats, but others will face extinction. Changes in climate can also disrupt ecosystems, leading to shifts in species composition and loss of biodiversity. This has implications for ecosystem services, such as pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration. Imagine a world without bees, or with entire forests disappearing – it's a scary thought.
Impacts on Agriculture and Food Security
Agriculture is highly sensitive to climate change. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events can all impact crop yields and livestock productivity. In some regions, climate change may lead to reduced agricultural productivity, while in others it may create new opportunities. However, the overall effect is likely to be negative, particularly in developing countries where agriculture is a major source of livelihood. This could lead to food shortages, price increases, and increased food insecurity.
Impacts on Human Health
Climate change can also have significant impacts on human health. Heatwaves can lead to heat stroke and other heat-related illnesses. Changes in air quality can exacerbate respiratory problems. Extreme weather events can cause injuries and displacement. Changes in disease vectors can lead to the spread of infectious diseases. Climate change can also have indirect effects on health, such as through malnutrition and mental health problems. Basically, climate change is bad for your body and your mind.
Regional Variations in Climate Impacts
Coastal Regions
Coastal regions are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Rising sea levels can lead to inundation of coastal areas, erosion of shorelines, and saltwater intrusion into freshwater resources. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and storm surges, can also cause extensive damage to coastal infrastructure. Many coastal communities are already experiencing the impacts of climate change, and these impacts are projected to worsen in the coming decades.
Arid and Semi-Arid Regions
Arid and semi-arid regions are already water-stressed, and climate change is projected to exacerbate these challenges. Changes in precipitation patterns can lead to more frequent and severe droughts, which can have devastating impacts on agriculture, livestock, and human health. Climate change can also lead to increased desertification and land degradation.
Mountain Regions
Mountain regions are also highly vulnerable to climate change. Rising temperatures can lead to melting glaciers and snowpack, which can alter water availability and increase the risk of floods and landslides. Changes in climate can also impact mountain ecosystems and biodiversity.
Polar Regions
Polar regions are warming at a faster rate than the rest of the planet. This is leading to melting sea ice and glaciers, which contributes to sea level rise. Changes in climate can also impact polar ecosystems and the indigenous communities that depend on them. The melting of permafrost can release large amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, which can further accelerate climate change.
Mitigating and Adapting to Climate Change
Mitigation: Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Mitigation refers to efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow down the rate of climate change. This can be achieved through a variety of strategies, including:
Transitioning to renewable energy sources: Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, is essential to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Improving energy efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industry can significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Protecting and restoring forests: Forests play a critical role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Protecting and restoring forests can help to mitigate climate change. Developing and deploying carbon capture technologies: Carbon capture technologies can capture carbon dioxide from power plants and other industrial sources and store it underground.
Adaptation: Preparing for the Impacts of Climate Change
Adaptation refers to efforts to prepare for the impacts of climate change that are already happening or are likely to happen in the future. This can be achieved through a variety of strategies, including:
Building seawalls and other coastal defenses: Coastal defenses can protect coastal communities from rising sea levels and storm surges. Developing drought-resistant crops: Drought-resistant crops can help to ensure food security in arid and semi-arid regions. Improving water management: Improving water management practices can help to conserve water and ensure that it is used efficiently. Strengthening public health systems: Strengthening public health systems can help to protect people from the health impacts of climate change.
The Role of Policy and International Cooperation
Addressing climate change requires a concerted effort from governments, businesses, and individuals. Policy plays a crucial role in setting emission reduction targets, promoting renewable energy, and incentivizing energy efficiency. International cooperation is essential to ensure that all countries are doing their part to address climate change.
FAQ: The Future Impacts of Climate Change: Projections
General Questions
What is the most concerning aspect of the future climate change projections?
Honestly, it's the interconnectedness of it all. It's not just one thing; it's the rising temperatures leading to sea-level rise, impacting agriculture, displacing populations, and exacerbating existing inequalities. It’s The Future Impacts of Climate Change: Projections showing us a cascading series of problems that could overwhelm our ability to cope.
Are the projections certain? Can we be sure about these predictions?
Climate models are constantly refined and based on the best available science, but they are not crystal balls. They provide a range of possible outcomes based on different scenarios. Think of it like a weather forecast – it’s usually pretty accurate, but sometimes Mother Nature throws a curveball. The further out the projections, the more uncertainty there is.
What is the worst-case scenario projected?
The worst-case scenario involves a significant increase in global temperatures, leading to catastrophic impacts on ecosystems, agriculture, and human health. This could include widespread droughts, floods, and extreme weather events, as well as sea levels rising several feet, displacing millions of people and inundating valuable infrastructure.
How soon will we start seeing these effects?
We're already seeing many of these effects! The increase in extreme weather events, like more intense hurricanes and longer-lasting droughts, are signs that the effects are underway. Many projections say that some of the more severe impacts will become increasingly apparent in the coming decades.
Specific Impact Questions
What impact will rising sea levels have on coastal cities?
Rising sea levels will inundate coastal areas, erode shorelines, and cause saltwater intrusion into freshwater resources. This could displace millions of people and damage coastal infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings. Some cities might even become uninhabitable.
How will agriculture be affected by these changes?
Changes in temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events can all impact crop yields and livestock productivity. In some regions, climate change may lead to reduced agricultural productivity, while in others it may create new opportunities. However, the overall effect is likely to be negative, particularly in developing countries where agriculture is a major source of livelihood.
What are the potential health impacts of climate change?
Climate change can lead to heat stroke, respiratory problems, injuries from extreme weather events, and the spread of infectious diseases. It can also have indirect effects on health, such as through malnutrition and mental health problems.
Action and Solutions
What can individuals do to help mitigate climate change?
Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint by conserving energy, using public transportation, eating less meat, and supporting policies that promote renewable energy and energy efficiency. Even small changes can make a big difference.
What role do governments play in addressing climate change?
Governments play a crucial role in setting emission reduction targets, promoting renewable energy, incentivizing energy efficiency, and investing in adaptation measures. International cooperation is also essential to ensure that all countries are doing their part to address climate change.
Is it too late to reverse the effects of climate change?
It's not too late to take action, but the window of opportunity is closing. The sooner we reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the more we can limit the impacts of climate change. Even if we can't completely reverse the effects, we can still significantly reduce the risks and protect future generations.
Conclusion
The Future Impacts of Climate Change: Projections paint a stark picture of the challenges we face. Rising temperatures, rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems and agriculture are all projected to have significant impacts on human society and the natural world. However, the future is not predetermined. By taking bold and decisive action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the changes that are already underway, we can still mitigate the worst impacts of climate change and create a more sustainable future. It requires a global effort, a commitment to innovation, and a willingness to prioritize the well-being of future generations. The time to act is now. It's not just about saving the planet; it's about saving ourselves.
.png)